Njavara is an important medicinal rice variety of Kerala, India, widely used in Ayurveda as a 'health food' and in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, paralysis, neurodegenerative diseases and in rejuvenation therapy. Phytochemical investigations and spectroscopic studies of the diethyl ether fraction of methanolic extract of Njavara Black (NB) rice bran gave three important compounds namely, tricin and two rare flavonolignans- tricin 4'-O-(erythro-β-guaiacylglyceryl) ether and tricin 4'-O-(threo-β-guaiacylglyceryl) ether. The EC(50) values of these compounds in DPPH system were 90.39, 352.04 and 208.1 μg/ml, respectively. Quantification of the compounds by HPLC in NB and staple, non-medicinal rice varieties Sujatha (SJ) and Palakkadan Matta (PM) showed that tricin is present 39.64 and 16.12 fold higher in NB, compared to SJ and PM, respectively. This is the first report on the occurrence of tricin at significantly higher levels in Njavara and occurrence of the two flavonolignans in Oryza sativa species. Of the three compounds, tricin and the threo- form of flavonolignan showed anti-inflammatory effect of >65% after 5 h, at 2 mg/kg, in carrageenan-induced, paw edema experiments in rats. The results of the study corroborate with the preferential use of Njavara in indigenous medicine, over staple varieties.

Another study elucidated the molecular mechanism of the notch pathway in vascular health and the role of NjRBO as a nutraceutical for the modulation of notch-mediated CD4+ Tcell activation in atherosclerotic rats. In this study, male Sprague-Dawley rats weighing 150-200g given standard diet formula were used. After the study duration of 60 days, in order to determine the nutraceutical effects of NjRBO, we sought to study the effects of treatment with NjRBO on notch pathway components in isolated splenic CD4+ T lymphocytes. In the present study, Western blot analysis revealed that upon high-fat diet supplementation resulted in T cell activation evidenced by increased CD28 co-receptor and CD25 marker expressions. In consistent with the above findings, we analyzed the mRNA expression pattern of Notch1, cleaved notch fragment, Notch-11C and Hes1, which showed a consistent up-regulation upon T-cell activation. Immunofluorescence assay also revealed an increase in Notch 1 receptor expression. Up-regulation in the expression of TCR-activated signalosome complexes or CBM complex in the diseased showed an increase indicating that Carma1-Bcl10-Malt1 (CBM) is a crucial event for T- cell receptor-induced NF-κB activation. Additionally, NF-қB translocation was enhanced in causing a concomitant alteration in Th1, Th2 transcription factors, T-bet, GATA-3 and its respective cytokines, IFN-γ and IL-4. Accordingly, we present evidence that Notch-regulated TCR-mediated activation of CD4+T-cell components was altered by NjRBO treatment, thereby revealing a novel role for the same in controlling TCR-mediated activation and inflammatory milieu.

Another study compares popular varieties of rice with Navara rice. In vitro starch digestibility and glycemic indices of three rice varieties- 'Njavara', 'Jyothi' (pigmented rice verities) and 'IR 64' (non-pigmented rice) with similar amylose content were studied. Starch digestibility studies showed differences in glycemic response in three types of rice. The rate of starch hydrolysis was maximum (67.3%) in 'Njavara' rice compared to other two rice varieties. 'Njavara' exhibited the lowest kinetic constant (k) indicating inherent resistance to enzymatic hydrolysis. The glycemic load (GL) and glycemic index (GI) of 'Njavara' were similar to 'Jyothi' and 'IR 64'. Resistant starch content was high in pigmented rice varieties compared to 'IR 64'. The resistant starch content of dehusked and cooked rice increased with the storage time at refrigeration temperature (4°C). 'Njavara' is an easily digestible rice and can be used for baby and geriatric foods.
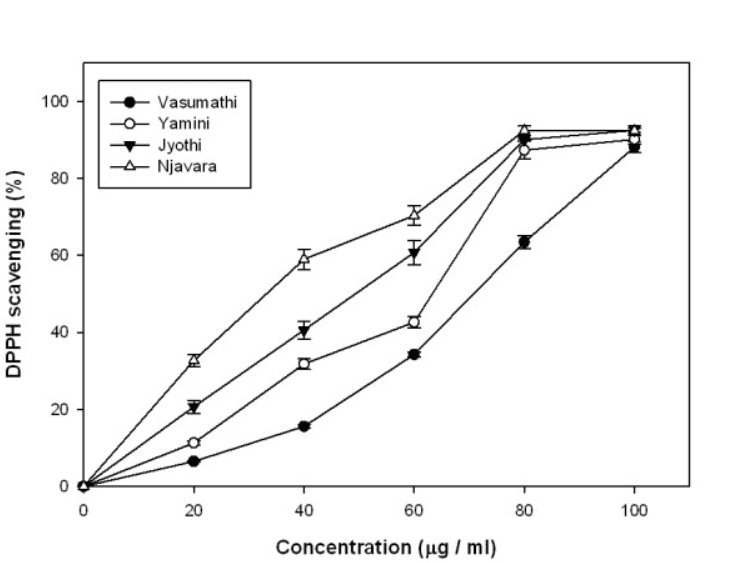
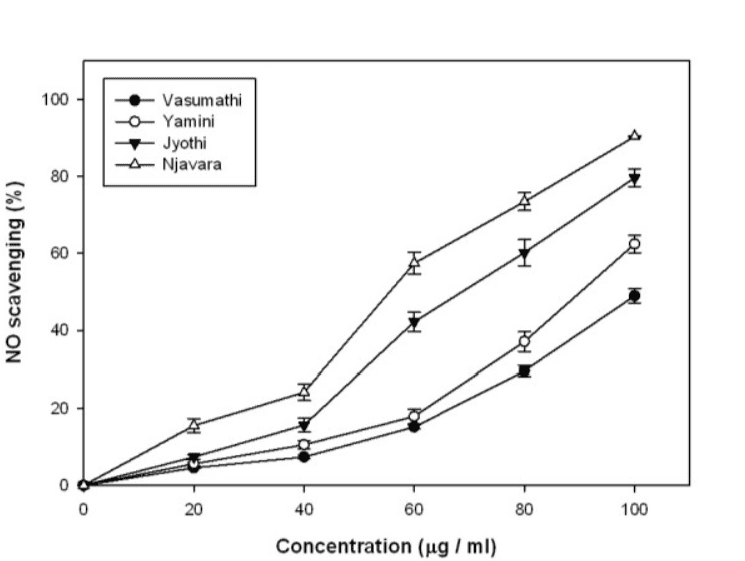
Another study details the antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of methanolic extracts from Navara Rice
Free radical-induced oxidative stress is the root cause for many human diseases. Naturally occurring antioxidant supplements from plants are vital to counter the oxidative damage in cells. The main objective of the present study was to characterize the antioxidant and antiproliferative potential of rice bran extracted from an important Indian rice variety, Njavara and to compare the same with two commercially available basmati rice varieties: Vasumathi, Yamini and a non medicinal variety, Jyothi.
Rice bran methanolic extract from Njavara showed the highest antioxidant and cell cytotoxic properties compared to the other three rice varieties. IC50 values for scavenging DPPH and nitric oxide were in the range of 30.85-87.72 microg/ml and 52.25-107.18 microg/ml respectively. Total antioxidant activity and reducing power were increased with increasing amounts of the extract. Total phenolic and flavonoid contents were in the range of 3.2-12.4 mg gallic acid-equivalent (GAE)/g bran and 1.68-8.5 mg quercetin-equivalent (QEE)/g bran respectively. IC50 values of cytotoxic assay (MTT assay) were 17.53-57.78 microg/ml. Correlation coefficient and regression analysis of phenolic content with DPPH and NO scavenging, MTT (-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide) assay, total antioxidant assay and reducing power showed a highly significant correlation coefficient values (96-99%) and regression values (91-98%).
Detailed Nutrition Facts:

Citations:
Rao AS, Reddy SG, Babu PP, Reddy AR. The antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of methanolic extracts from Njavara rice bran. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2010 Jan 28;10:4. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-10-4. PMID: 20109194; PMCID: PMC2823621.
Deepa G, Venkatachalam L, Bhagyalakshmi N, Shashidhar HE, Singh V, Naidu KA. Physicochemical and genetic analysis of an endemic rice variety, Njavara (Oryza sativa L.), in comparison to two popular South Indian cultivars, Jyothi (PTB 39) and IR 64. J Agric Food Chem. 2009 Dec 23;57(24):11476-83. doi: 10.1021/jf902052p. PMID: 19924858.
Lal Preethi Ss, Sabu V, Helen A. Njavara rice (Oryza sativa Linn.) bran oil exerts anti-inflammatory effects through regulation of Notch-mediated T-cell receptor (TCR) activation in experimentally induced atherosclerosis. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2022 Sep 30;68(10):21-29. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2022.68.10.4. PMID: 37114276.